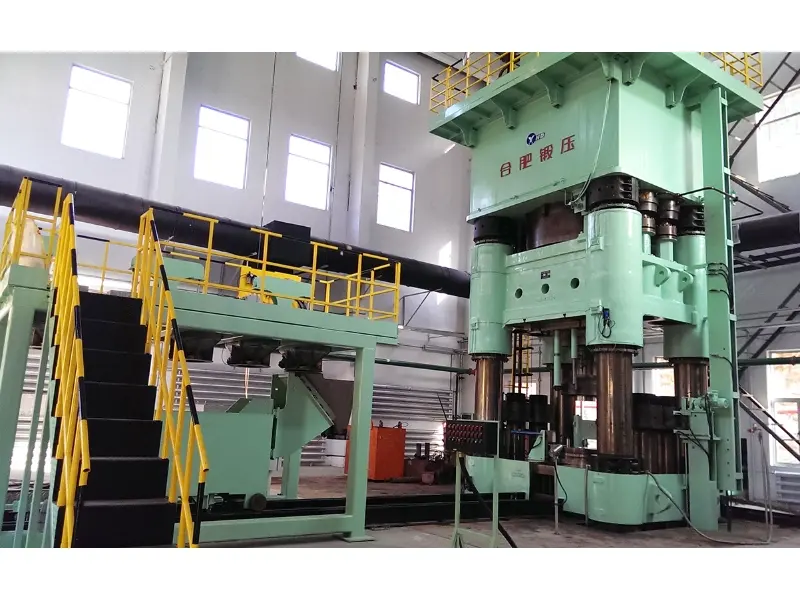
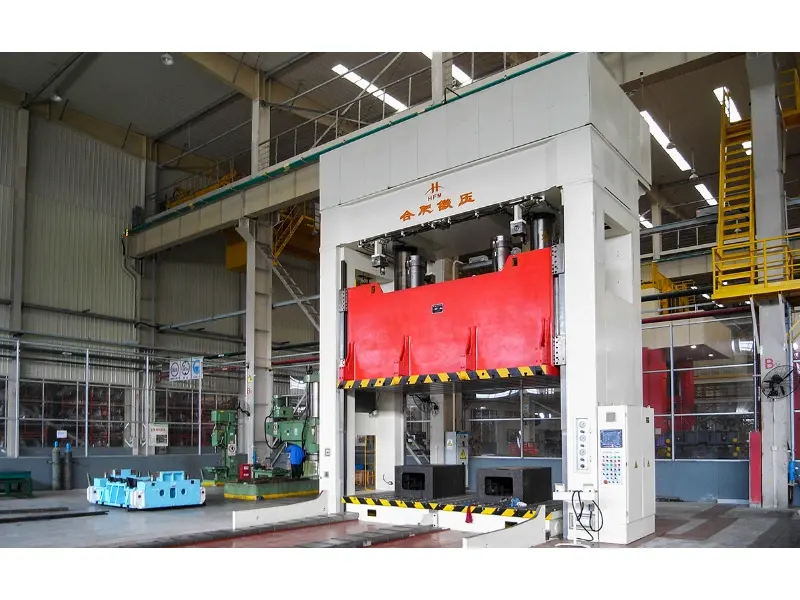
Mechanical Press: A Complete Guide to Its Functionality and Applications
Release time: 2026-01-19
Table of Contents
In manufacturing and mechanical engineering, the mechanical press is a key tool that has revolutionized the way materials are processed and shaped. This guide aims to explain the operating principles of the mechanical press, its functionality, applications, and the scientific basis for its operation.
What is a mechanical press?
Mechanical press A press is a machine that uses mechanical advantage to apply significant force to a workpiece, typically for shaping, cutting, or molding materials. A press operates on the principle of leverage, using a system of gears, levers, and a flywheel to amplify the force applied by the operator. This allows for the efficient processing of metals, plastics, and other materials in a variety of production environments.
How does a mechanical press work?
At its core, a mechanical press consists of several key components: a frame, a ram, a die, and a drive mechanism. The frame provides structural support, while the ram is the moving part that descends to apply pressure to the workpiece. The die, mounted on the press frame, forms the material as the ram descends.
Operation begins when the operator activates the drive mechanism, often a flywheel connected to the crankshaft. As the flywheel rotates, it converts rotary motion into linear motion, causing the ram to move downward. The mechanical advantage created by gears and levers allows the press to apply forces that can exceed several tons, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications.
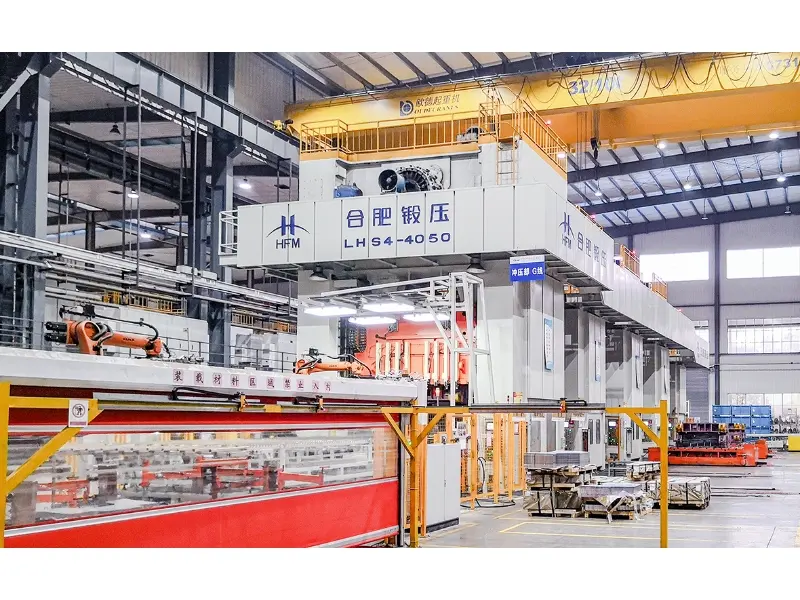
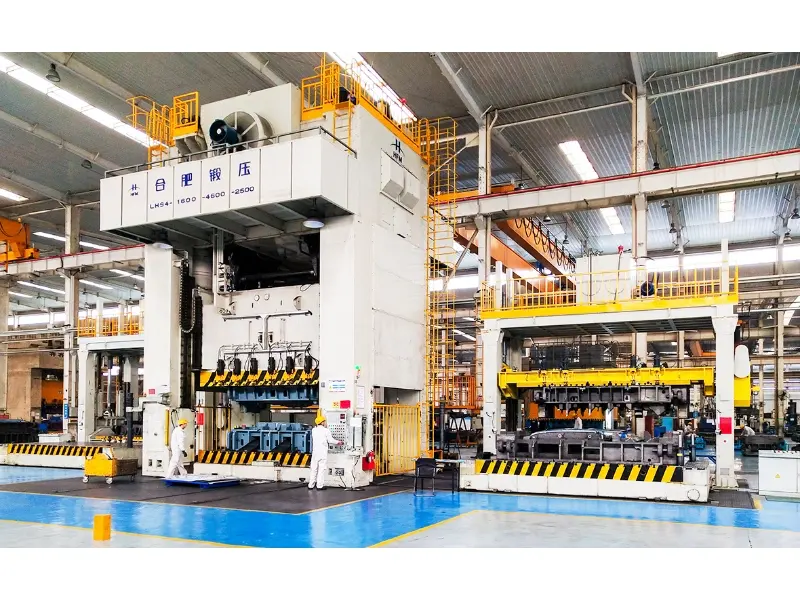


Application of mechanical presses
Mechanical presses These are versatile machines used in a variety of industries. Here are some of the most common applications:
Metal Forming: One of the primary applications of mechanical presses is metal forming processes such as stamping, bending, and punching. These processes are essential in the automotive and aerospace industries, where precision and strength are paramount.
Plastic molding: Mechanical presses are also used in the production of plastic components. By applying heat and pressure, manufacturers can create complex shapes and designs to meet specific requirements.
Assembly operations: On assembly lines, mechanical presses are used to join components together, ensuring reliable and efficient assembly of parts.
Minting and Forging: The mechanical press plays a vital role in the minting process, where metal is formed into coins or medallions. Similarly, it is used in forging operations to create strong and durable components.
Advantages of mechanical presses
A mechanical press has several advantages over other types of presses, such as hydraulic presses. These include:
Speed: Mechanical presses can operate at higher speeds, increasing production efficiency.
Precision: The mechanical design ensures consistent and repeatable results, which is crucial in high-volume production.
Cost-effective: Mechanical presses generally require less maintenance and have lower operating costs than hydraulic systems.
Conclusion
Mechanical press The mechanical press is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, combining engineering principles and practical applications to create a wide range of products. Understanding its functionality and applications not only highlights its importance across various industries but also demonstrates the ingenuity of mechanical engineering. Whether you're a seasoned engineer or an inquisitive enthusiast, the mechanical press is a fascinating topic that embodies the intersection of science and engineering. As we continue to innovate and refine manufacturing processes, the mechanical press will undoubtedly remain an essential tool in our industrial arsenal.