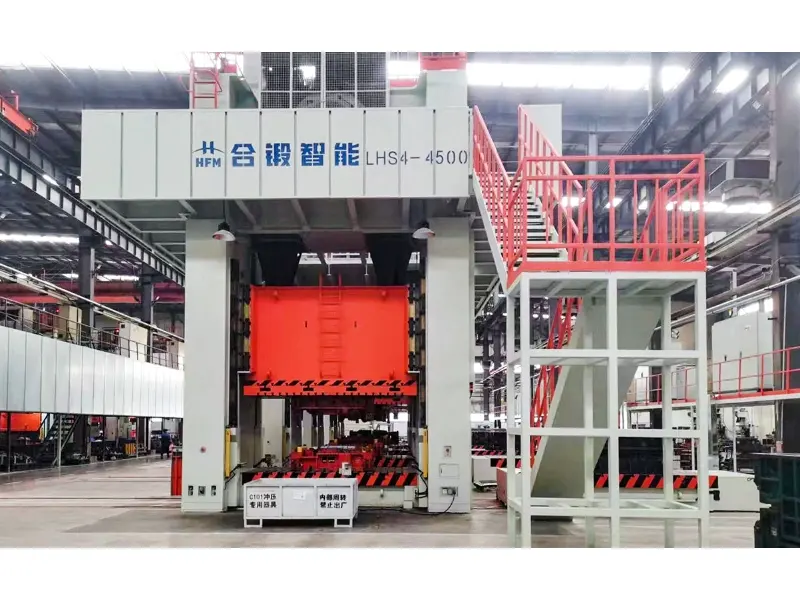
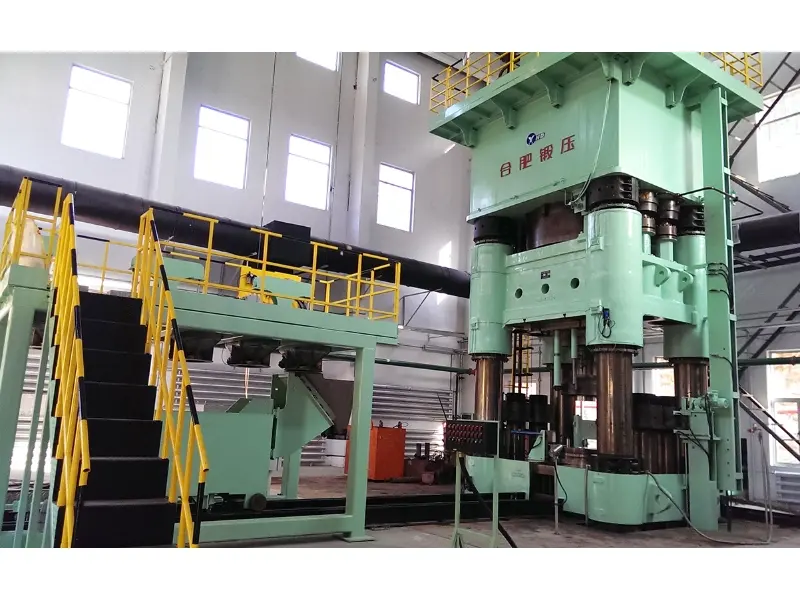
Three types of forging presses
Release time: 2025-11-20
Introduction
Pressing is an important technology in the manufacturing industry where force is applied to shape and process metals. Pressing machines Forging presses play a key role in the forging process, acting on the workpiece to deform it into the desired shape. In this article, we will examine the three main types of forging presses: mechanical presses, hydraulic presses, and screw presses, highlighting their features, advantages, and applications.

Mechanical presses
Mechanical presses are driven by a motor connected to a flywheel that stores energy. When the flywheel is activated, it releases the stored energy, driving a piston (the upper die), which strikes the workpiece, creating the desired deformation. Key features of mechanical presses include:
- High speed: Mechanical presses operate at high speed, making them ideal for mass production.
- Fine tuning: These presses provide precise control of the impact force, allowing for high accuracy in forming complex parts.
- Versatility: Mechanical presses can be used for various types of forging, including open and closed forging.
Application areas: Mechanical presses are widely used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods manufacturing to produce components such as gears, bolts, and fasteners.
Hydraulic presses
Hydraulic presses Hydraulic presses use hydraulic cylinders to generate and control the force applied to the workpiece. Hydraulic fluid is pumped into the cylinders, creating pressure that moves a piston rod, exerting force on the material. Key features of hydraulic presses include:
- High impact force: Hydraulic presses can generate very high levels of force, making them suitable for heavy forging operations.
- Adjustable pressure: The pressure generated by hydraulic presses can be easily adjusted, allowing for flexible adaptation to the forming of different types of metals.
- Safety: Hydraulic presses are equipped with safety systems such as overload protection and emergency stop buttons to ensure operator safety during operation.
Application areas: Hydraulic presses are widely used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and oil and gas to produce components such as crankshafts, connecting rods, and valves.
Screw presses
Screw presses use a flywheel to drive a screw mechanism, which applies pressure to the workpiece. As the flywheel rotates, the screw moves downward, applying pressure to the material. Key features of screw presses include:
- Low speed: Screw presses operate at lower speeds than mechanical presses, making them ideal for precision forging.
- Energy efficiency: These presses consume less energy due to their slow operation, which allows for significant cost savings.
- High control: Screw presses provide precise control over the forging process, allowing for high forming accuracy and minimizing material loss.
Application areas: Screw presses are used in industries such as aerospace, defense, and specialty tooling to produce high-precision components with complex shapes.
Conclusion
Mechanical pressesHydraulic presses, and screw presses are the three main types of forging presses widely used in the manufacturing industry. Each type has its own unique features, advantages, and applications. Understanding the capabilities of each type helps companies select the most suitable option for their production needs, resulting in improved efficiency and product quality.